Tau function and dysfunction in Alzheimer disease
Research summary:
Tau is a neuronal protein involved, directly or indirectly, in different neuronal functions. Tau dysfunction could result in neurodegenerative disorders, tauopathies, being Alzheimer disease the most relevant one. Tau functions depend on its subcellular localization and binding to specific neuronal components. Our objective is to analyze these tau functions and possible new ones. We have analyzed the structural and functional differences between human and mouse tau proteins by focusing in an extra aminoacid sequence only present in human tau, that has a function in axonal transport of some proteins, also we have studied the secretion mechanism that results in the presence of extracellular tau, or the role of tau protein in the localization of NMDA extrasynaptic receptors. Since tau is a phosphoprotein mainly modified by GSK3b kinase, we have studied the consequences of GSK3b overexpression in neuronal cell.
Mainly, in the group headed by Dr. Hernández, the role of tau presence in glia cells (oligodendrocytes, astrocytes and microglia) was analyzed, and it was also found that different cell surface receptors could be involved in the interaction of extracellular tau with neurons or with glia cells.
Finally, our group has done several collaborations with other groups located inside or outside of the CBMSO, in aspects related to Alzheimer disease or other neurodegenerative disorders or aging. About aging, we have described the rejuvenation of some old granule neurons, located at hippocampal area upon expression of the reprogramming (Yamanaka) factors.
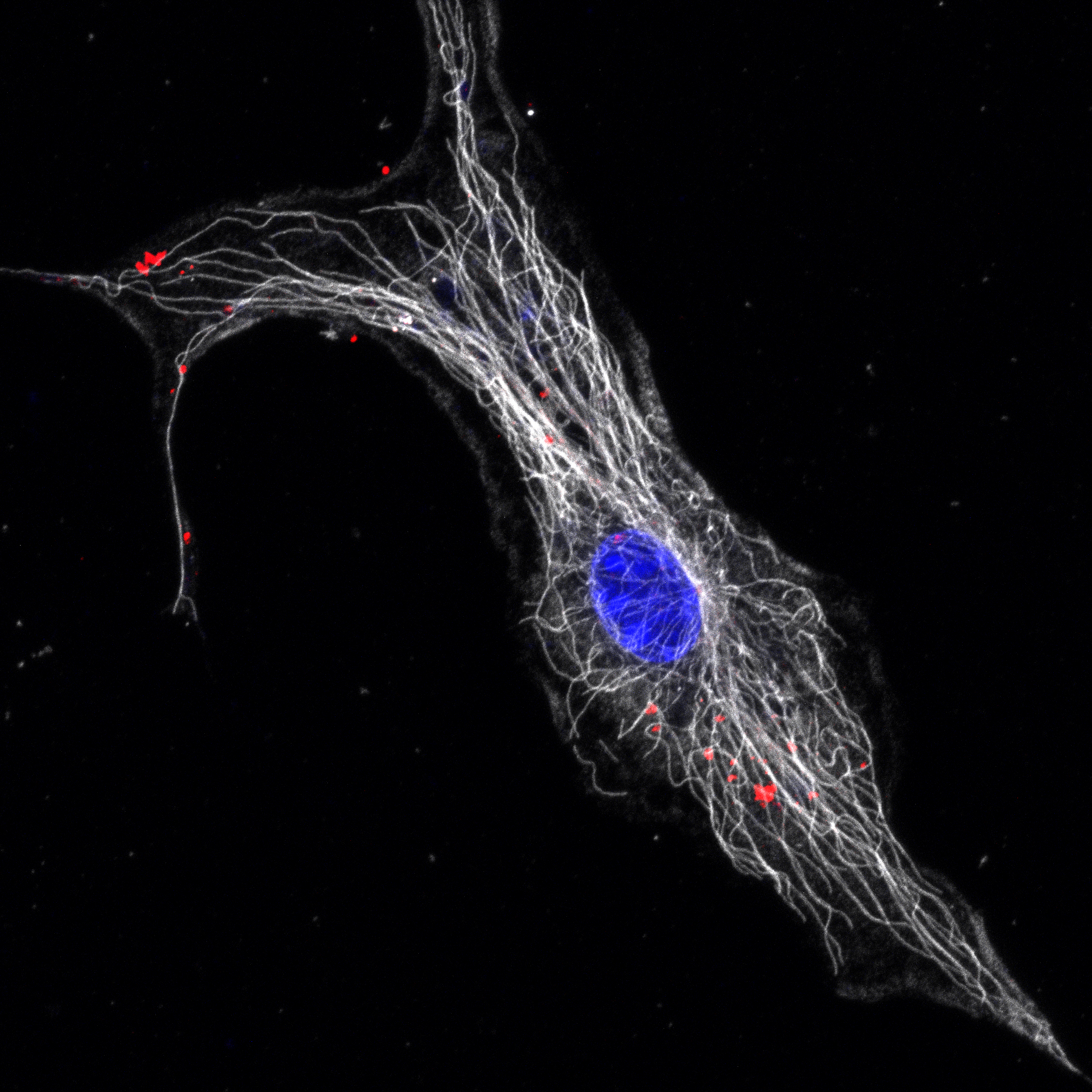
Figure 1 - Microglia internalizing extracellular tau protein (red). The white signal corresponds to the microtubules of the cell.
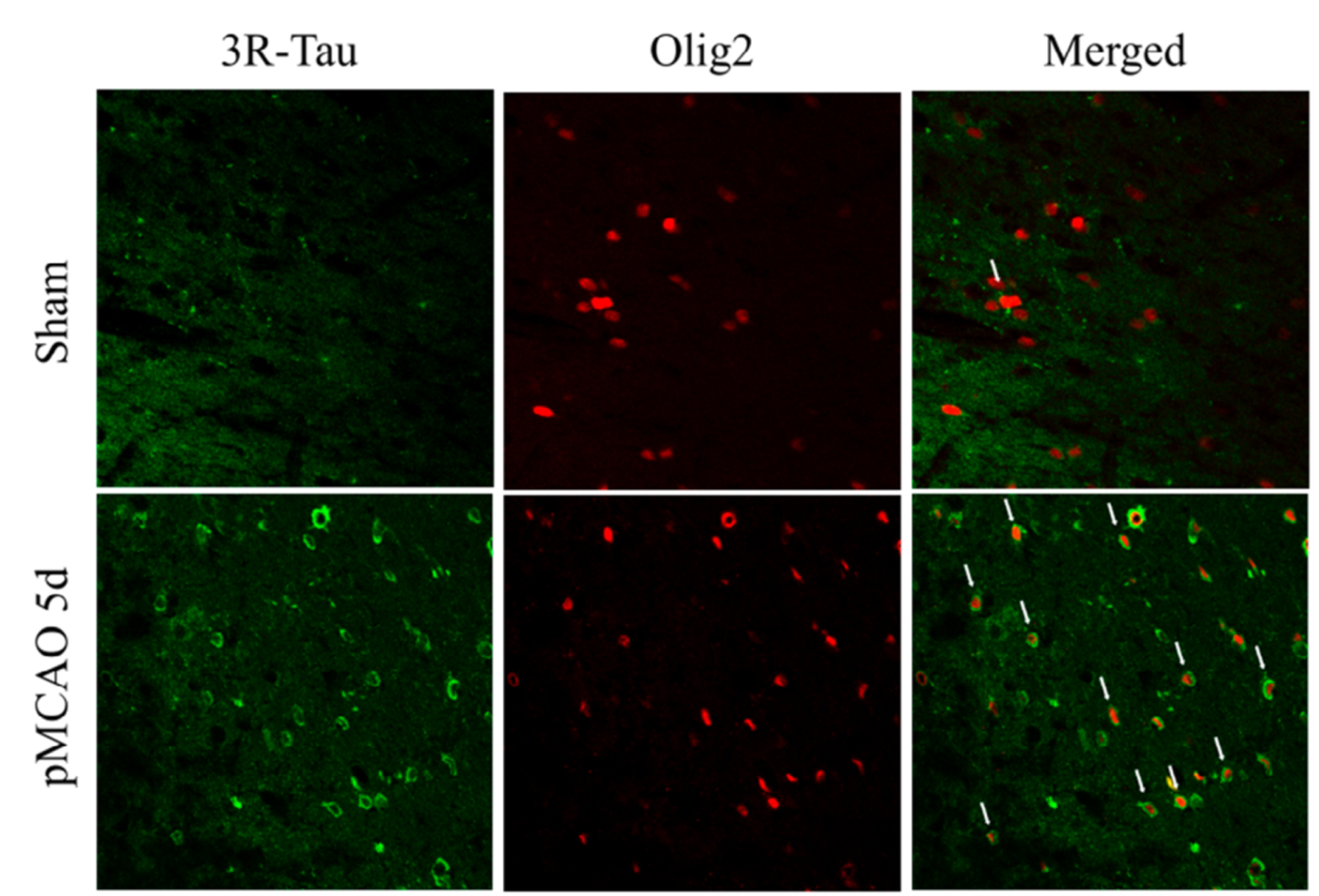
Figure 2 - Focal cerebral ischemia (pMCAO) induces an increase 3R-Tau isoform in oligodendrocytes in the damaged area.

| Last name | Name | Laboratory | Ext.* | Professional category | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antón Fernández | Alejandro | 208 | 4803 | aanton(at)cbm.csic.es | Doctor FC3 |
| Ávila de Grado | Jesús | 208 | 4564 | javila(at)cbm.csic.es | Doctor Vinculado "Ad Honorem" |
| Cuadros Catalán | Raquel | 208 | 4592 | rcuadros(at)cbm.csic.es | E. Técnicos Especializados de Organismos Públicos de Investigación |
| Domene Serrano | Indalo | 208 | 4592 | Estudiante TFM | |
| García-Escudero Barreras | Vega | 208 | 4592 | vescudero(at)cbm.csic.es | Profesor Titular Universidad, GA |
| Gómez Ramos | Alberto | 208 | 4592 | alberto.gomez(at)csic.es | Contratado CIBER |
| Martín López | Gerardo | 209 | 4552 | Contrato Predoctoral | |
| Medina Padilla | Miguel | 208 | 4592 | Contratado CIBER | |
| Stoliarov Radushinskaya | Anastasia | 208 | 4592 | Estudiante TFM | |
| Torre Alonso | Nuria de la | 208 | 4803 | ndelatorre(at)cbm.csic.es | M2 66,66% |
| Vallés Saiz | Laura | 208 | 4592 | laura.valles(at)cbm.csic.es | Doctor FC3 |
Relevant publications:
-
Avila, J. & Perry, G. (2021) A Multilevel View of the Development of Alzheimer's Disease, Neuroscience. 457, 283-293.
-
Villa Gonzalez, M., Valles-Saiz, L., Hernandez, I. H., Avila, J., Hernandez, F. & Perez-Alvarez, M. J. (2020) Focal cerebral ischemia induces changes in oligodendrocytic tau isoforms in the damaged area, Glia. 68, 2471-2485.
-
Rodriguez-Matellan, A., Avila, J. & Hernandez, F. (2020) Overexpression of GSK-3beta in Adult Tet-OFF GSK-3beta Transgenic Mice, and Not During Embryonic or Postnatal Development, Induces Tau Phosphorylation, Neurodegeneration and Learning Deficits, Front Mol Neurosci. 13, 561470.
-
Perez, M., Hernandez, F. & Avila, J. (2020) Protein Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease at Different Stages of Neurodegeneration, Int J Mol Sci. 21.
-
Perea, J. R., Bolos, M. & Avila, J. (2020) Microglia in Alzheimer's Disease in the Context of Tau Pathology, Biomolecules. 10.
-
Hernandez, F., Merchan-Rubira, J., Valles-Saiz, L., Rodriguez-Matellan, A. & Avila, J. (2020) Differences Between Human and Murine Tau at the N-terminal End, Front Aging Neurosci. 12, 11.
-
Gargini, R., Segura-Collar, B., Herranz, B., Garcia-Escudero, V., Romero-Bravo, A., Nunez, F. J., Garcia-Perez, D., Gutierrez-Guaman, J., Ayuso-Sacido, A., Seoane, J., Perez-Nunez, A., Sepulveda-Sanchez, J. M., Hernandez-Lain, A., Castro, M. G., Garcia-Escudero, R., Avila, J. & Sanchez-Gomez, P. (2020) The IDH-TAU-EGFR triad defines the neovascular landscape of diffuse gliomas, Sci Transl Med. 12.
-
Garcia-Arriaza, J., Marin, M. Q., Merchan-Rubira, J., Mascaraque, S. M., Medina, M., Avila, J., Hernandez, F. & Esteban, M. (2020) Tauopathy Analysis in P301S Mouse Model of Alzheimer Disease Immunized With DNA and MVA Poxvirus-Based Vaccines Expressing Human Full-Length 4R2N or 3RC Tau Proteins, Vaccines (Basel). 8.
-
Avila, J. (2020) The Role of TGF-beta1 in Promoting Microglial Abeta Phagocytosis, Neuroscience. 438, 215-216.
-
Sayas, C. L., Medina, M., Cuadros, R., Olla, I., Garcia, E., Perez, M., Ferrer, I., Hernandez, F. & Avila, J. (2019) Role of tau N-terminal motif in the secretion of human tau by End Binding proteins, PLoS One. 14, e0210864.
-
Perez, M., Avila, J. & Hernandez, F. (2019) Propagation of Tau via Extracellular Vesicles, Front Neurosci. 13, 698.
-
Perea, J. R., Lopez, E., Diez-Ballesteros, J. C., Avila, J., Hernandez, F. & Bolos, M. (2019) Extracellular Monomeric Tau Is Internalized by Astrocytes, Front Neurosci. 13, 442.
-
Pallas-Bazarra, N., Draffin, J., Cuadros, R., Antonio Esteban, J. & Avila, J. (2019) Tau is required for the function of extrasynaptic NMDA receptors, Sci Rep. 9, 9116.
-
Merchan-Rubira, J., Sebastian-Serrano, A., Diaz-Hernandez, M., Avila, J. & Hernandez, F. (2019) Peripheral nervous system effects in the PS19 tau transgenic mouse model of tauopathy, Neurosci Lett. 698, 204-208..
-
Kenny, A., Jimenez-Mateos, E. M., Zea-Sevilla, M. A., Rabano, A., Gili-Manzanaro, P., Prehn, J. H. M., Henshall, D. C., Avila, J., Engel, T. & Hernandez, F. (2019) Proteins and microRNAs are differentially expressed in tear fluid from patients with Alzheimer's disease, Sci Rep. 9, 15437.
-
Jurado-Arjona, J., Rodriguez-Matellan, A., Avila, J. & Hernandez, F. (2019) GSK3beta overexpression driven by GFAP promoter improves rotarod performance, Brain Res.
-
Jadhav, S., Avila, J., Scholl, M., Kovacs, G. G., Kovari, E., Skrabana, R., Evans, L. D., Kontsekova, E., Malawska, B., de Silva, R., Buee, L. & Zilka, N. (2019) A walk through tau therapeutic strategies, Acta Neuropathol Commun. 7, 22.
-
Hernandez, F., Cuadros, R., Olla, I., Garcia, C., Ferrer, I., Perry, G. & Avila, J. (2019) Differences in structure and function between human and murine tau, Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1865, 2024-2030.
- Pallas-Bazarra, N., Avila, J. & Llorens-Martin, M. (2019) Maturation dynamics of the axon initial segment (AIS) of newborn dentate granule cells in young adult C57BL/6J mice, J Neurosci.
Doctoral theses:
- Noemí Pallas Bazarra (2015).Estudio del papel de la proteína tau en la modulación de la neurogénesis hipocampal adulta. Universidad Autónoma de Madrid. Directores: María Llorens-Martín y Félix Hernández.
- Patricia Martín-Maestro (2016). Mitophagy dysfunction in peripherasl and neural models of Alzheimer disease. Universidad Autónoma de Madrid. Directores: Vega García-Escudero y Jesús Avila.




















